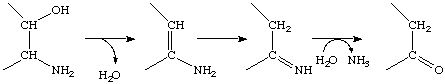
EC 4. Lyases
Lyases are enzymes cleaving C-C, C-O, C-N and other bonds by other means than by hydrolysis or oxidation. They differ from other enzymes in that two substrates are involved in one reaction direction, but only one in the other direction. When acting on the single substrate, a molecule is eliminated and this generates either a new double bond or a new ring. The systematic name is formed according to 'substrate group-lyase'. In common names, expressions like decarboxylase, aldolase, etc. are used. 'Dehydratase' is used for those enzymes eliminating water. In cases where the reverse reaction is the more important, or the only one to be demonstrated, 'synthase' may be used in the name.
EC 4.1 Carbon-Carbon Lyases
This subclass contains the decarboxylases (EC 4.1.1), the aldehyde-lyases catalysing the reversal of an aldol condensation (EC 4.1.2), and the oxo-acid-lyases, catalysing the cleavage of a 3-hydroxy acid (EC 4.1.3), or the reverse reactions.
EC 4.2 Carbon-Oxygen Lyases
These enzymes catalyse the breakage of a carbon-oxygen bond. In the case of hydro-lyases (EC 4.2.1), this is by elimination of water; in sub-subclass EC 4.2.2 it is by the elimination of an alcohol from a polysaccharide and in sub-subclass EC 4.2.3 it is by elimination of a phosphate. A few other cases are grouped in EC 4.2.99.
EC 4.3 Carbon-Nitrogen Lyases
This subclass contains the enzymes that release ammonia or one of its derivatives, with the formation of a double bond or ring. Some catalyse the actual elimination of the ammonia, amine or amide, e.g.
Others, however, catalyse elimination of another component, e.g. water, which is followed by spontaneous reactions that lead to breakage of the C-N bond, e.g.
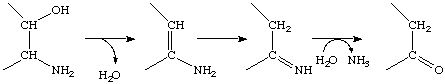
as in EC 4.3.1.17 (L-serine ammonia-lyase), so that the overall reaction is
i.e., an elimination with rearrangement. The sub-subclasses of EC 4.3 are the ammonia-lyases (EC 4.3.1), lyases acting on amides, amidines, etc. (EC 4.3.2), the amine-lyases (EC 4.3.3), and other carbon-nitrogen lyases (EC 4.3.99).
EC 4.4 Carbon-Sulfur Lyases
Enzymes eliminating H2S or substituted H2S; a single sub-subclass EC 4.4.1.
EC 4.5 Carbon-Halide Lyases
This subclass was originally set up on the basis of the enzyme eliminating HCl from DDT.
EC 4.6 Phosphorus-Oxygen Lyases
The so-called 'nucleotidyl-cyclases' are included here, on the basis that diphosphate is eliminated from the nucleoside triphosphate.
EC 4.99 Other Lyases
A subclass of miscellaneous enzymes.
Return to Enzymes Home Page.