Peroxiredoxin
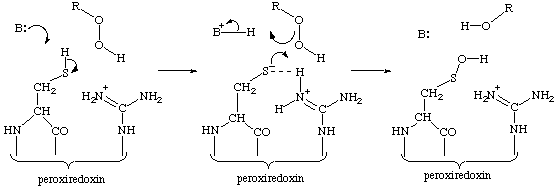
Mechanism for formation of sulfenic acid
The mechanism below rationalizes the reaction mechanism of the formation of the sulfenic acid, see Wood, Z.A., Schröder, E., Harris, J.R. and Poole, L.B. Structure, mechanism and regulation of peroxiredoxins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28 (2003) 32-40. [PMID: 12517450]
© IUBMB 2004