Citric acid cycle
When cursor points to a box further details will be displayed in a tooltip window. If you click on the box you will change to appropriate reaction scheme or enzyme specification.
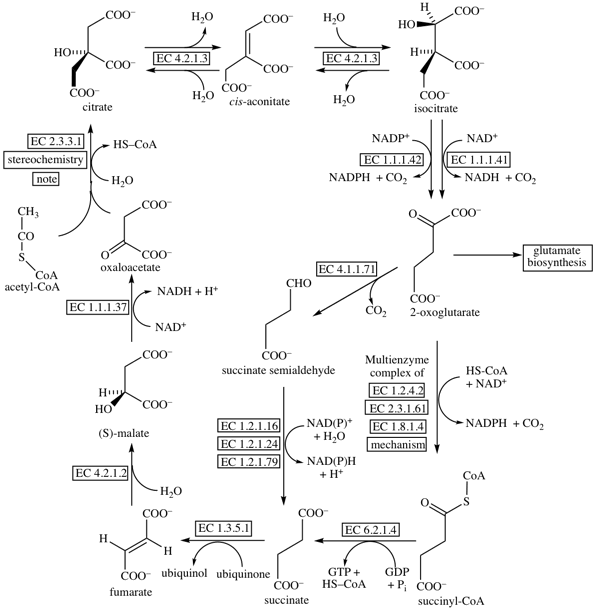
© IUBMB 2003
When cursor points to a box further details will be displayed in a tooltip window. If you click on the box you will change to appropriate reaction scheme or enzyme specification.

© IUBMB 2003
enzymes homepage.
stereochemistry of EC 2.3.3.1 citrate (Si)-synthase
oxo-acid dehydrogenase complex reactions
glutamate biosynthesis
EC 1.1.1.37 malate dehydrogenase
EC 1.1.1.41 isocitrate dehydrogenase (NAD+)
EC 1.1.1.42 isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+)
EC 1.2.1.16 succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase [NAD(P)+]
EC 1.2.1.24 succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (NAD+)
EC 1.2.1.79 succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (NADP+)
EC 1.2.4.2 oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (succinyl-transferring)
EC 1.3.5.1 succinate dehydrogenase (ubiquinone)
EC 1.8.1.4 dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase
EC 2.3.1.61 dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase
EC 2.3.3.1 citrate (Si)-synthase
EC 4.1.1.71 2-oxoglutarate decarboxylase
EC 4.2.1.2 fumarate hydratase
EC 4.2.1.3 aconitate hydratase
EC 6.2.1.4 succinate-CoA ligase (GDP-forming)