EC 2.6.1
L-α-Amino Acid Transaminases
(Using 2-oxoglutarate/L-glutamate)
When cursor points to a box further details will be displayed in a tooltip window. If you click on the box you will change to the appropriate enzyme specification.
| Reaction | |
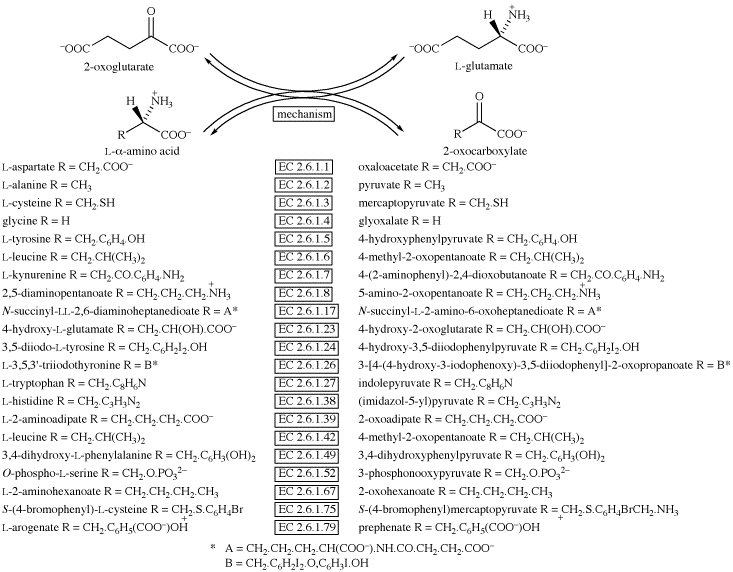 | |
| © IUBMB 2005 | |
See also other transamination reactions using pyruvate/L-alanine or glyoxalate/glycine or phenylpyruvate/L-phenylalanine or miscellaneous 2-oxo acids/L-α-amino acids.
See Nomenclature and symbolism for amino acids and peptides for more details of α-amino acid structures.
Return to:
enzymes homepage.
EC 2.6.1 transamination mechanism
EC 2.6.1.1 aspartate transaminase
EC 2.6.1.2 alanine transaminase
EC 2.6.1.3 cysteine transaminase
EC 2.6.1.4 glycine transaminase
EC 2.6.1.5 tyrosine transaminase (another illustration and another)
EC 2.6.1.6 leucine transaminase (another illustration)
EC 2.6.1.7 kynurenine—oxoglutarate transaminase (another illustration)
EC 2.6.1.8 2,5-diaminovalerate transaminase
EC 2.6.1.17 succinyldiaminopimelate transaminase (another illustration)
EC 2.6.1.23 4-hydroxyglutamate transaminase
EC 2.6.1.24 diiodotyrosine transaminase
EC 2.6.1.26 thyroid-hormone transaminase
EC 2.6.1.27 tryptophan transaminase
EC 2.6.1.38 histidine transaminase
EC 2.6.1.39 2-aminoadipate transaminase (another illustration)
EC 2.6.1.42 branched-chain-amino-acid transaminase (another illustration and another and another)
EC 2.6.1.49 dihydroxyphenylalanine transaminase
EC 2.6.1.52 phosphoserine transaminase (another illustration)
EC 2.6.1.67 2-aminohexanoate transaminase
EC 2.6.1.75 cysteine-conjugate transaminase
EC 2.6.1.79 glutamate—prephenate aminotransferase
